A la suite de notre tuto Comment déployer .net 5 api sur linux Ubuntu 20.04 (Nginx) -Linode (Partie 1).
Nous allons ajouter un nom de domaine pour notre api dotnet et ajouter un certificat SSL pour activer https.
Let’s go…..
Achetons un nom de domaine « testlinode.com » sur Hostinger
J’utilise Hostinger pour acheter les noms de domaine. Je trouve les services de Hostinger rapide, avec un service client très réactif.
Rendez vous sur le site hostinger.
Sur mon Panel je vais sur domaine et je tape « testlinode » sa sera notre nom de domaine pour ce tuto. Nous effectuons le paiement en utilisant notre carte de crédit.
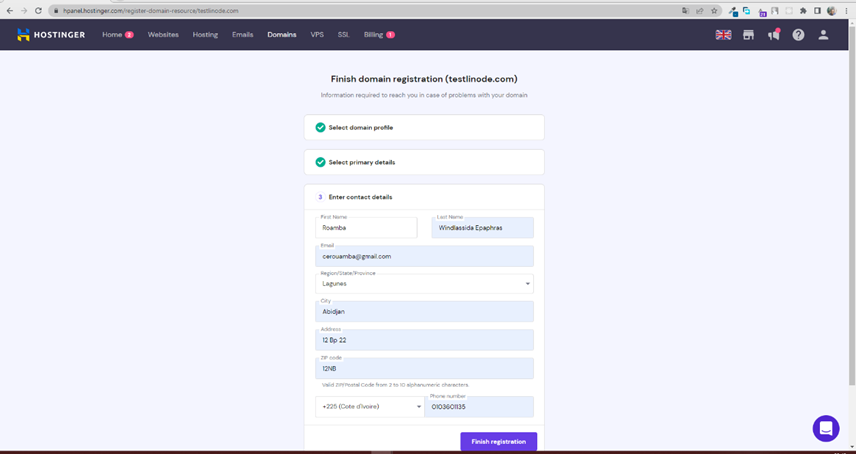
Ensuite renseignons nos informations pour le nom de domaine
Après avoir renseigné nos informations, notre nom de domaine est maintenant disponible.
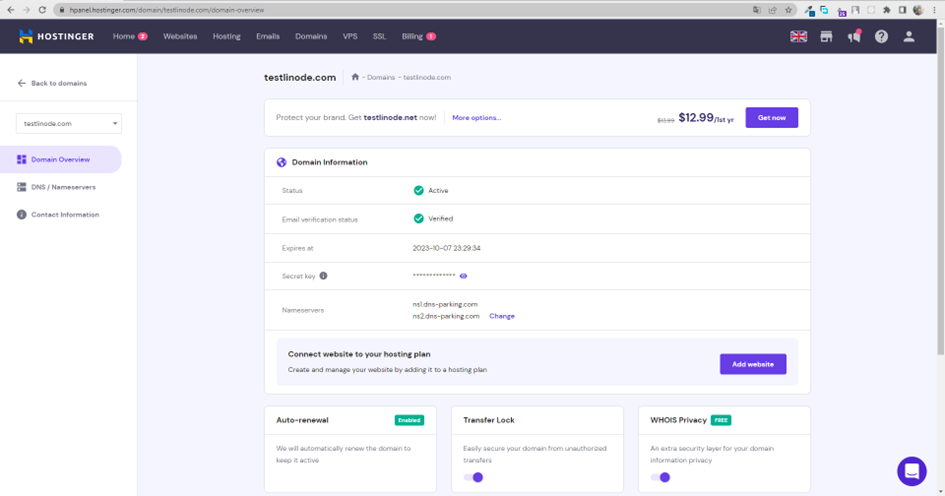
Notre nom de domaine est aussi disponible en ligne
Revenons sur le dashboard de notre nom de domaine
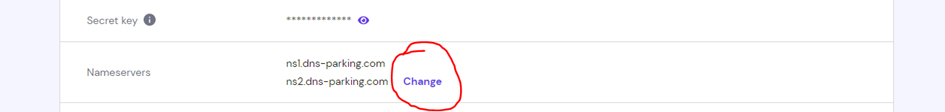

Ajoutons l’adresse IP de notre machine Ubuntu
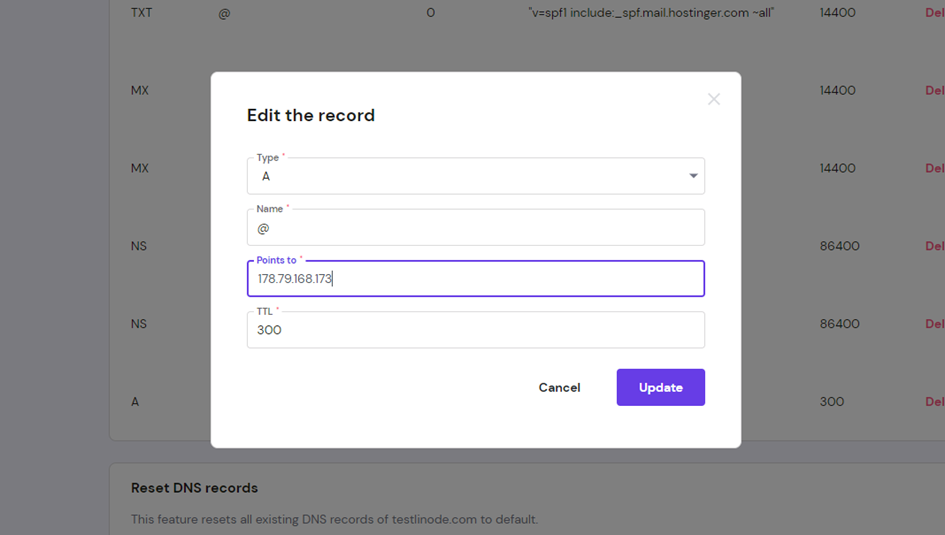
Nous pouvons tester maintenant notre serveur nom de domaine sur Hostinger. Il est bien lié à notre machine sur linode.
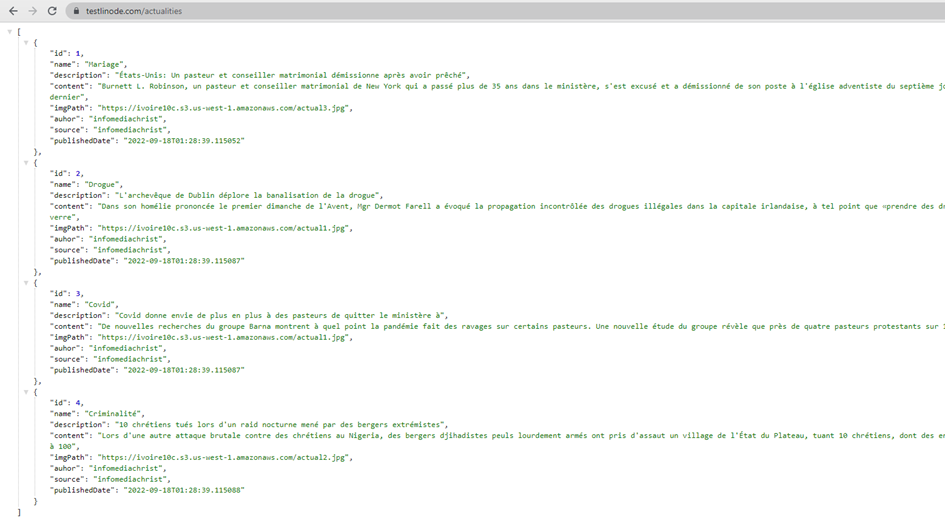
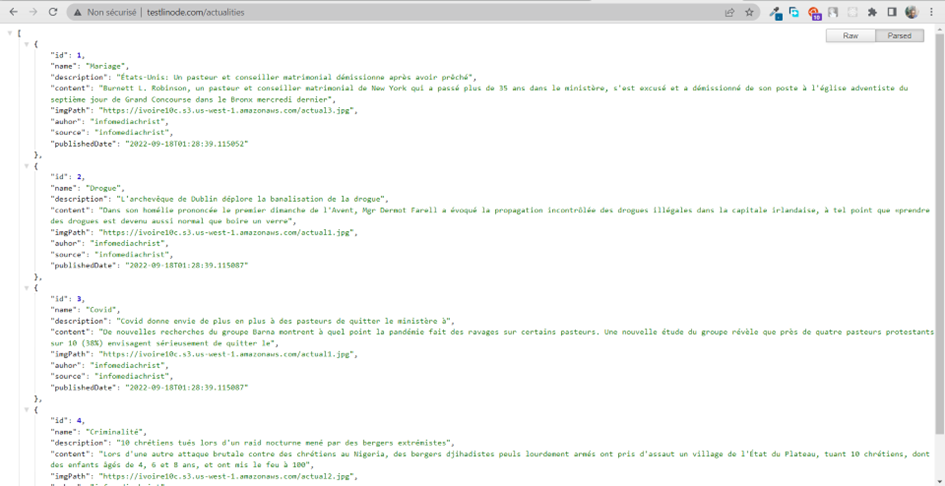
Testons l'endpoint http://testlinode.com/actualities
Maintenant ajoutons un certificat ssl .
HTTPS est un moyen sécurisé d'envoyer des données entre un serveur Web et un navigateur Web.
Commençons par la configuration pour passer de http à https sur notre serveur linode Ubuntu
D’abord sur notre projet dotnet nous allons effectuer quelques configurations pour passer à HTTPS
Dans notre fichier Program.cs
public static IHostBuilder CreateHostBuilder(string[] args) =>
Host.CreateDefaultBuilder(args)
.ConfigureWebHostDefaults(webBuilder =>
{
webBuilder.UseStartup<Startup>().UseUrls("https://testlinode.com:5000;http://testlinode.com:5002").UseKestrel();
// webBuilder.UseStartup<Startup>().UseUrls("http://localhost:5000");
});
Ensuite dans notre fichier Startup.cs
app.UseHsts();
Et dans notre fichier appsettings.json
"Kestrel": {
"Endpoints": {
"Http": {
"Url": "http://testlinode.com:5002"
},
"Https": {
"Url": "https://testlinode.com:5000"
}}}
Faisons un rebuild du projet
D:\PROJET\BACK DOTNET\CHRETIEN 2\CHRETIEN2> dotnet build
Maintenant utilisons FileZilla pour le transfert vers notre machine Ubuntu 20.Utilisons une connexion FTP avec le port 22.On supprime d’abord les anciens fichiers
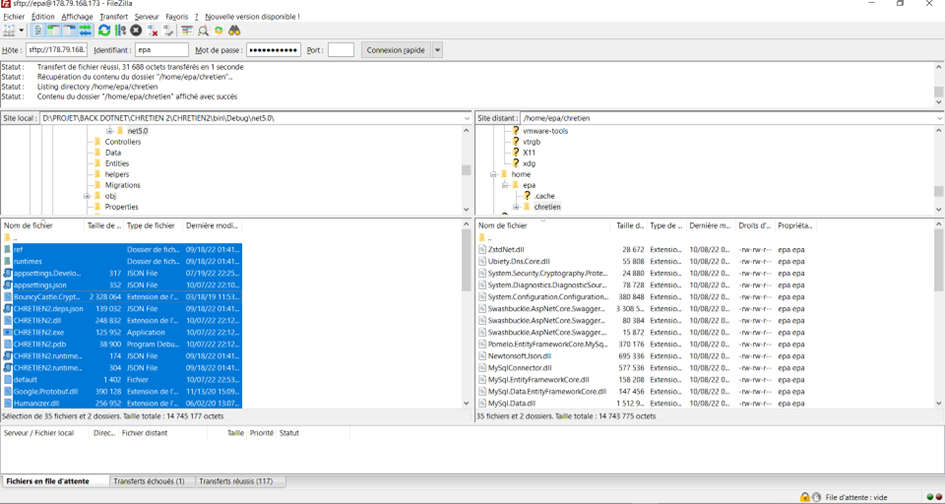
Générons le certificat pour notre nom de domaine
Activons https avec ufw
sudo ufw allow https
Installation de certificat SSL
epa@localhost:~/chretien$ sudo apt install -y certbot
epa@localhost:~/chretien$ sudo certbot certonly --standalone -d testlinode.com -d www.testlinode.com
ou
sudo certbot certonly --standalone -d www.testlinode.com
ou
sudo certbot certonly --standalone -d testlinode.com
Modifions également notre fichier de configuration Nginx
epa@localhost:~/chretien$ sudo vim /etc/nginx/sites-available/default
Remplaçons le contenu par la nouvelle configuration Nginx pour https
server {
listen 80;
server_name testlinode.com;
return 301 https://$host$request_uri;
}
server {
listen 443;
server_name testlinode.com;
ssl_certificate /etc/letsencrypt/live/www.testlinode.com/fullchain.pem;
ssl_certificate_key /etc/letsencrypt/live/www.testlinode.com/privkey.pem;
ssl on;
ssl_session_cache builtin:1000 shared:SSL:10m;
ssl_protocols TLSv1 TLSv1.1 TLSv1.2;
ssl_ciphers HIGH:!aNULL:!eNULL:!EXPORT:!CAMELLIA:!DES:!MD5:!PSK:!RC4;
ssl_prefer_server_ciphers on;
gzip on;
gzip_http_version 1.1;
gzip_vary on;
gzip_comp_level 6;
gzip_proxied any;
gzip_buffers 16 8k;
gzip_disable “MSIE [1-6].(?!.*SV1)”;
location / {
proxy_pass https://178.79.168.173:5000;
proxy_http_version 1.1;
proxy_set_header Upgrade $http_upgrade;
proxy_set_header Connection keep-alive;
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_cache_bypass $http_upgrade;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Proto $scheme;
}
}Redémarrons Nginx
epa@localhost:~$ sudo systemctl restart nginx
Créons un service pour lancer notre projet en arrière-plan
epa@localhost:~$ sudo vim /etc/systemd/system/CHRETIEN2.service
Ajoutons la configuration suivante
[Unit]
Description= Example .NET Web API App running on Ubuntu
[Service]
WorkingDirectory=/home/epa/chretien
ExecStart=/usr/bin/dotnet /home/epa/chretien/CHRETIEN2.dll
Restart=always
# Restart service after 10 seconds if the dotnet service crashes:
RestartSec=10
SyslogIdentifier=CHRETIEN2
User=root
Environment=ASPNETCORE_ENVIRONMENT=Production
Environment=DOTNET_PRINT_TELEMETRY_MESSAGE=false
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.targetepa@localhost:~$ sudo systemctl enable CHRETIEN2.service
epa@localhost:~$ sudo systemctl start CHRETIEN2.service

Enfin nous avons terminé, l’activation d’un certificat ssl sur un projet .net en production .
Maintenant le certificat https est activé